5 Stages of Tooth Decay What They Are and How to Treat Them
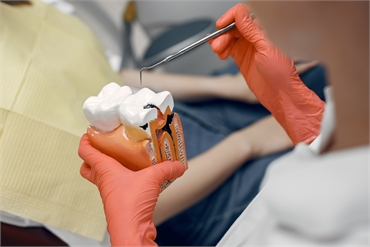
Learn about the five stages of tooth decay, from initial demineralization to abscess formation, and how to treat and prevent them.
Tooth decay is a common dental problem that affects millions of people around the world.
It occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acid that erodes the hard outer layer of the teeth, called enamel.
Over time, this can lead to cavities, pain, infection, and tooth loss.
In this blog post, we will explain the five stages of tooth decay, how they affect your oral health, and how you can treat them.
5 Stages of Tooth Decay
Stage 1: Initial demineralization
The first stage of tooth decay is called initial demineralization. This is when the enamel loses some of its minerals due to acid exposure. This can happen when you eat or drink sugary or acidic foods and drinks, or when you have poor oral hygiene.
You may not notice any symptoms at this stage, but you may see white spots on the surface of your teeth. These are signs of weakened enamel that can be easily damaged.
Treatment:
The good news is that this stage is reversible. You can help your enamel remineralize by using fluoride toothpaste, mouthwash, or supplements. Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens the enamel and protects it from acid.
You can also stimulate the production of saliva, which is a natural defense against acid and bacteria. You can do this by drinking water, chewing sugar-free gum, or eating crunchy fruits and vegetables.
Stage 2: Enamel decay
The second stage of tooth decay is called enamel decay. This is when the enamel breaks down further and forms cavities or holes in the teeth. This can happen when the acid exposure is too frequent or too long, and the enamel cannot repair itself.
You may start to experience symptoms such as tooth sensitivity, pain, or discoloration. You may also notice black or brown spots on your teeth. These are signs of decayed enamel that can be easily infected.
Treatment:
This stage is irreversible. You cannot restore the enamel once it is lost. You need to visit your dentist as soon as possible to get dental fillings. Dental fillings are materials that fill the cavities and restore the tooth structure. They also prevent bacteria from entering the tooth and causing more damage. Dental fillings can be made of different materials, such as composite resin, amalgam, gold, or porcelain.
Stage 3: Dentin decay
The third stage of tooth decay is called dentin decay. This is when the dentin, the softer layer under the enamel, is affected by acid and bacteria. Dentin is more vulnerable to decay than enamel, because it has tiny tubes that connect to the pulp, the innermost layer of the tooth. When the dentin is decayed, the bacteria can reach the pulp and cause inflammation and infection.
You may experience symptoms such as severe tooth sensitivity, pain, or difficulty chewing. You may also notice changes in the shape or size of your tooth. These are signs of damaged dentin that can compromise the tooth function.
Treatment:
The treatment for this stage depends on the extent of the decay and the condition of the pulp. If the pulp is still healthy, you may only need a larger filling or a crown to cover the tooth. A crown is a cap that fits over the tooth and protects it from further damage.
However, if the pulp is infected, you may need a root canal treatment. A root canal treatment is a procedure that removes the infected pulp and replaces it with a rubber-like material. This saves the tooth from extraction and prevents the infection from spreading.
Stage 4: Pulp damage
The fourth stage of tooth decay is called pulp damage. This is when the pulp, the innermost layer of the tooth, is severely inflamed and infected. The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels that provide nutrients and sensations to the tooth. When the pulp is damaged, the tooth becomes dead and loses its ability to heal.
You may experience symptoms such as intense pain, swelling, fever, or bad breath. You may also notice pus or blood coming out of the tooth or the gums. These are signs of a dying tooth that can endanger your overall health.
Treatment:
The treatment for this stage is usually extraction or surgery. Extraction is the removal of the tooth from the socket. This eliminates the source of infection and relieves the pain. However, it also leaves a gap in your mouth that can affect your appearance, speech, and chewing.
You may need a replacement tooth, such as a denture, a bridge, or an implant. Surgery is the removal of the infected tissue and bone around the tooth. This preserves the tooth and prevents the infection from spreading. However, it also involves cutting and stitching the gums and may require a longer recovery time.
Stage 5: Abscess formation
The fifth and final stage of tooth decay is called abscess formation. This is when an abscess, a pus-filled pocket, forms at the end of the tooth root. An abscess is a serious complication that can result from untreated pulp damage. It can cause severe pain, swelling, and fever, and can spread the infection to the surrounding bone and tissues. If left untreated, it can lead to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis or facial cellulitis.
You may experience symptoms such as throbbing pain, swollen face, difficulty breathing or swallowing, or nausea. You may also notice a foul-smelling or tasting discharge from the tooth or the gums. These are signs of a dangerous infection that requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment:
The treatment for this stage is antibiotics and drainage. Antibiotics are drugs that kill the bacteria and stop the infection. Drainage is the removal of the pus from the abscess. This can be done by making a small incision in the gum or by performing a root canal treatment. Both treatments are essential to relieve the pressure and pain and to prevent further complications.
Conclusion
Tooth decay is a progressive disease that can affect your oral and general health. It has five stages, each with different symptoms and treatments.
The best way to prevent tooth decay is to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing, flossing, rinsing, avoiding sugary foods and drinks, and visiting the dentist in Brampton regularly.
By doing so, you can keep your teeth healthy and beautiful for a lifetime.

