Moon Molars—What Causes It?
July 09, 2022
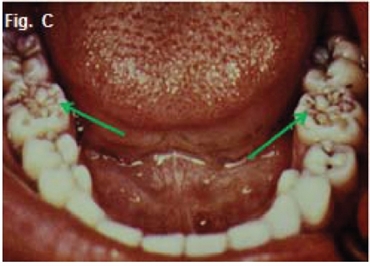
Moon molars are small, dome-shaped first molars. The enamel on moon molars tends to be poorly developed and the grinding surface of the tooth often has many small cusps instead of the usual four. These are also known as mulberry molars or Fournier molars. And the condition has been decidedly linked to congenital syphilis.
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a chronic infectious disease. It is caused by a bacterium called Treponema pallidum and is highly contagious. In adults, the most common way to contract the disease is contact with an infected person’s syphilis sore, usually during sexual activity. It can also be spread by swimming pools, hot tubs, bathtubs, toilet seats, and shared clothing. Syphilis can also be passed on to a baby during pregnancy or the birthing process. This is called congenital syphilis.
How does syphilis affect babies?
Congenital syphilis can harm the baby, cause several different symptoms, or even cause death. This is why the CDC recommends women be tested for syphilis at least once during pregnancy—preferably during their first prenatal visit. With quick diagnosis and treatment, syphilis is curable.
How syphilis affects a baby’s health largely depends on when the mother acquired syphilis and when she received treatment. Approximately 40% of children born to women with untreated syphilis are stillborn (die before delivery) or die shortly after birth. If the baby survives, those born with congenital syphilis often develop bone damage, tooth damage, enlarged liver and spleen, nerve problems, skin rashes, or severe anemia.
Treatment options for syphilis
Penicillin is an effective treatment for syphilis. And pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis should receive immediate treatment because early treatment is key in preventing lasting effects in children. Ideally, the infection should be treated before the eighteenth week of pregnancy. The mother’s sexual partner(s) should also get treatment to help prevent re-infection. If the patient is allergic to penicillin they can receive antibiotic like doxycycline. In the early stages of syphilis, one dose of penicillin or another antibiotic is usually sufficient. In later stages of the disease, the patient may require more doses.
Treatment options for early congenital syphilis
Surviving infants with early congenital syphilis should be evaluated at birth and assessed for additional treatment. They should be closely monitored following delivery, whether treatment was provided for the mother or not. An infected baby could be born without symptoms but could develop serious symptoms in the first few weeks. For treatment, newborns are given penicillin intravenously or intramuscularly. For eye inflammation, they can receive corticosteroid and atropine drops. And children with hearing loss might benefit from a corticosteroid taken by mouth.
Infants who remain undiagnosed and untreated can progress to late congenital syphilis. And symptoms often present themselves after age five. These are the results of scarring from early systemic disease or persistent inflammation. These often present in teeth, bones, eyes, skin, or mucous membranes. A few characteristics of late congenital syphilis can include bone pain, boney abnormalities, inflammatory lesions of the cornea, eighth nerve deafness, and dental abnormalities like moon molars.

